GUI简介
Gui的核心技术: Swing AWT
1.因为界面不美观。
2.需要jre环境!
所以并不流行
为什么我们要学习?
1.可以写出自己心中想要的一些小工具
2.工作时候,也可能需要维护到swing界面,概率极小!
3.了解MVC架构,了解监听!
AWT
1.包含了很多类和窗口,GUI
2.元素:窗口,按钮,文本框
3.java.awt
创建自己的第一个Frame窗口
public class TestFrame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//建立自己的一个Frame窗口
Frame frame = new Frame("这是我的第一个frame窗口");
//让frame窗口从内存中显示出来
frame.setVisible(true);
//设置长宽
frame.setSize(400,400);
//设置窗口的初始位置
frame.setLocation(250,250);
//设置背景颜色
frame.setBackground(new Color(187,222,145));
//设置窗口不可拉伸
frame.setResizable(false);
}
}

坑一、我们发现窗口点X关不掉,只能以停止程序运行的方式关掉
创建多个弹窗:
public class TestFrame02 {
//设置多个弹窗
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyFrame myFrame1 = new MyFrame(100,100,200,200,Color.blue);
MyFrame myFrame2 = new MyFrame(300,100,200,200,Color.yellow);
MyFrame myFrame3 = new MyFrame(100,300,200,200,Color.red);
MyFrame myFrame4 = new MyFrame(300,300,200,200,Color.green);
}
}
class MyFrame extends Frame{
static int id = 0;//用于计数多个窗口的数量
public MyFrame(int x,int y,int w,int h,Color color){
super("MyFrame+"+(++id));//这是每个窗口的题目
setBackground(color);
setBounds(x,y,w,h);
setVisible(true);
}
}
Panel面板
面板不能单独存在,它是基于Frame而存在的,它存在于某个容器内部,创建一个面板:
public class panel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame();
Panel panel = new Panel();
//设置布局
frame.setLayout(null);
//设置frame坐标
frame.setBounds(300,300,500,500);
frame.setBackground(new Color(40,160,77));
//设置panel位置,它的位置是相对于frame的
panel.setBounds(50,50,400,400);
panel.setBackground(new Color(193,15,60));
//往frame里面添加panel
frame.add(panel);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
效果图:
现在解决上面的坑——点X关闭不了窗口,实现起来简单,只需要添加监听事件,监听窗口关闭事件需要注意,addWindowListener()里面的参数就不要是new WindowListener了,原因是new WindowListener需要重写十几种方法,而在这里我们只需要实现关闭窗口的功能,所以只需要拿WindowListener的一个子类WindowAdapter就可以了,而这就是适配器模式。
//添加监听事件,监听窗口关闭事件
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {//适配器
//结束进程
System.exit(0);
}
});
布局管理器
- 流式布局:
public class TestFlowLayOut {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//流式布局
Frame frame = new Frame();
Button button1 = new Button("button1");
Button button2 = new Button("button2");
Button button3 = new Button("button3");
//设置流式布局
//frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout());//默认居中
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
//frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT));
//frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
frame.add(button1);
frame.add(button2);
frame.add(button3);
frame.setSize(200,200);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
- 东西南北中
public class TestBorderLayout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new 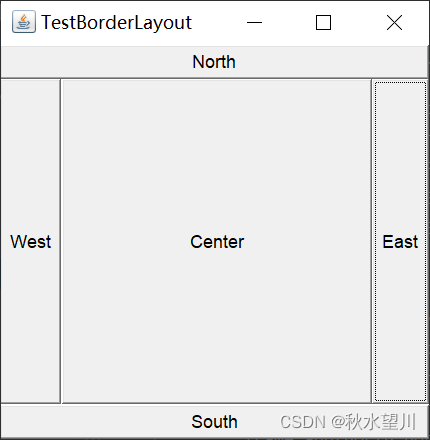
Frame("TestBorderLayout");
Button east = new Button("East");
Button west = new Button("West");
Button south = new Button("South");
Button north = new Button("North");
Button center = new Button("Center");
frame.add(east,BorderLayout.EAST);
frame.add(west,BorderLayout.WEST);
frame.add(south,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.add(north,BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(center,BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setSize(300,300);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
- 表格布局Grid
public class TestGridLayout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("TestGridLayout");
Button btn1 = new Button("btn1");
Button btn2 = new Button("btn2");
Button btn3 = new Button("btn3");
Button btn4 = new Button("btn4");
Button btn5 = new Button("btn5");
Button btn6 = new Button("btn6");
frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(3,2));
frame.add(btn1);
frame.add(btn2);
frame.add(btn3);
frame.add(btn4);
frame.add(btn5);
frame.add(btn6);
frame.pack();//这个函数的作用是让这六个表格自适应填充
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
事件监听
public class TestActionEvent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//事件监听,监听按下按钮,触发一些事件
Frame frame = new Frame();
Button button = new Button();
//因为addActionlistener()需要一个Actionlistener,所以我们创建一个Actionlistener
MyActionListener myActionListener = new MyActionListener();
button.addActionListener(myActionListener);
frame.add(button,BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
windowClose(frame);
}
//自定义一个关闭窗口事件
private static void windowClose(Frame frame){
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
class MyActionListener implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("aaa");
}
}
- 输入框TextField事件监听
public class TestText01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyFrame01();//启动
}
}
class MyFrame01 extends Frame{
public MyFrame01(){
TextField textField = new TextField();
add(textField);
//监听这个文本框输入的文字
MyActionListener2 myActionListener2 = new MyActionListener2();
textField.addActionListener(myActionListener2);
//设置替换编码,使得输入的文本编程*号
textField.setEchoChar('*');
setVisible(true);
pack();
}
}
class MyActionListener2 implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
TextField field = (TextField)e.getSource();
System.out.println(field.getText());
//设置回车之后文本框的内容变为空
field.setText("");
}
}
oop原则:组合大于继承!
class A extends B{
}
class A{
public B b;//这就是组合
}
一个简易计算器
public class TestCalc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyCalculator();
}
}
class MyCalculator extends Frame{
public MyCalculator(){
TextField num1 = new TextField(10);
TextField num2 = new TextField(10);
TextField num3 = new TextField(20);
Button button = new Button("=");
Label label = new Label("+");
//给button添加监听事件
button.addActionListener(new MyCalculatorListener(num1,num2,num3));
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
add(num1);
add(label);
add(num2);
add(button);
add(num3);
pack();
setVisible(true);
}
}
class MyCalculatorListener implements ActionListener{
private TextField num1,num2,num3;
//添加一个构造器获取三个参数
public MyCalculatorListener(TextField num1,TextField num2,TextField num3){
this.num1=num1;this.num2=num2;this.num3=num3;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int n1=Integer.parseInt(num1.getText());
int n2=Integer.parseInt(num2.getText());
num3.setText(""+(n1+n2));
//清除前两个框
num1.setText("");
num2.setText("");
}
}
这里的代码能用组合类的知识进行优化,但推荐更好的内部类知识进行包装,面向对象编程嘛,但我懒得写了。
结尾语:兄弟们,后面的东西跟前面的就很像了,基本看一遍视频就能掌握,以后有时间了我就回来补一下剩下的笔记。个人觉得后面以及前面的这些窗口啥的用前端来做会更加的合适,而且内容与前端有点类似。我就继续下一环节了_。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
文章由极客之音整理,本文链接:https://www.bmabk.com/index.php/post/99080.html


